Mensuration
Mensuration is a division of mathematics that studies geometric figure calculation and its parameters such as area, length, volume, lateral surface area, surface area, etc. It outlines the principles of calculation and discusses all the essential equations and properties of various geometric shapes and figures.
History of Mensuration
The Ancient Egyptians created and developed effective methods for land surveying, leveling, and mensuration, and have used mathematics to deal with these methods of mensuration. Mensuration is a branch of mathematical science that is concerned with the measurement of areas and volumes of various geometric figures.
Mensuration Formulae
Mensuration is a branch of mathematics that deals with measurements such as
- Length
- Perimeter
- Area
- Curved / Lateral surface area
- Surface area
- Volume
of various 2D & 3D geometric shapes and figures.
Perimeter (P): Length of the boundary of the given shape
Area (A): Surface enclosed by a given shape. (It is measured in sq. units)
Volume (V): Space occupied by a solid or a 3D object. (It is measured in Cu. units)
Curved Surface Area / Lateral Surface Area (CSA)
Area enclosed by the curved portion of a geometrical object.
Total Surface Area (TSA): Sum of the areas of all the surfaces of an object.
Some 3D Solids
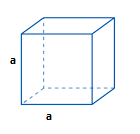
Cube
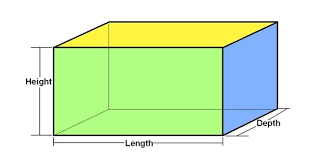
Cuboid
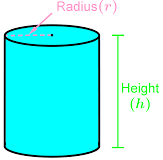
Right Circular Cylinder
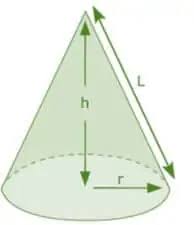
Right Circular Cone
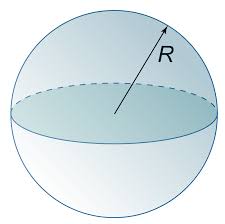
Sphere
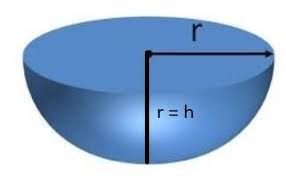
Hemisphere
| Solids | Dimensions | CSA | TSA | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cube(8 Vertices & 12 Edges) |
Side = a |
4a2 |
6a2 |
a3 |
Cuboid(8 Vertices & 12 Edges) |
Length = l |
2h (l + b) |
2(lb+bh+lh) |
lbh |
Right Circular Cylinder |
Radius of the base = r |
2πrh |
2πr(h+r)
|
πr2h |
Sphere |
Radius = r |
4πr2 |
4πr2 |
(4/3) πr3 |
Hemisphere |
Radius = r |
2πr2 |
3πr2 |
(2/3) πr3 |
Right Circular Cone |
Radius of the base = r |
πrl l = √(r2+ h2) |
πr(l+r) |
(1/3) πr2h |
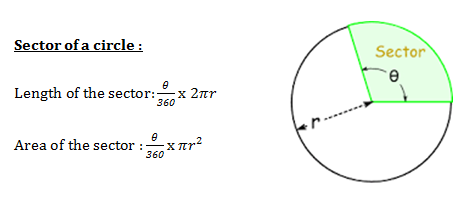
Author’s Creation in Mensuration
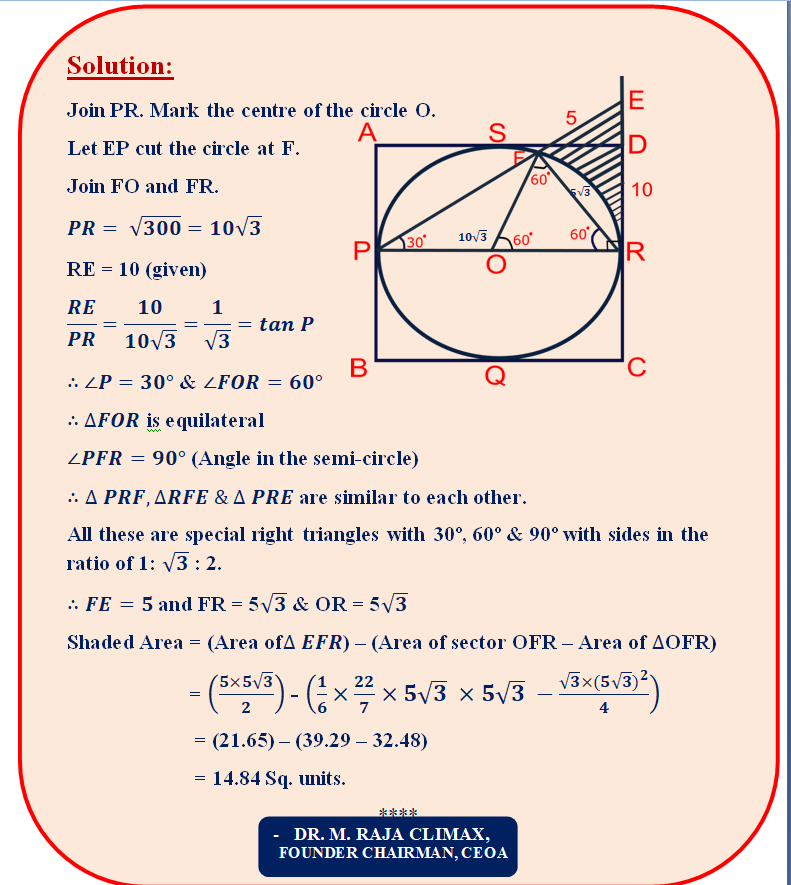
1. Question:
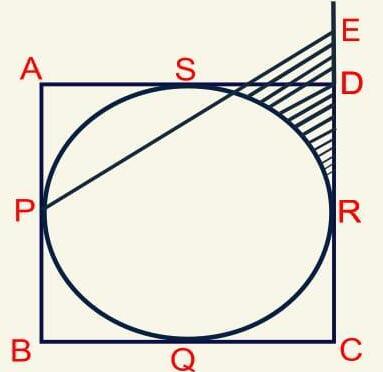
ABCD is a square with area 300 sq.units. A circle is inscribed inside the square ABCD, as shown in the picture, touching its sides at P,Q,R and S. RD is produced to E such that RE = 10 units and EP is joined. Find the area of the shaded portion.
Problem created by
- Dr.M.Raja Climax,
FOUNDER CHAIRMAN, CEOA
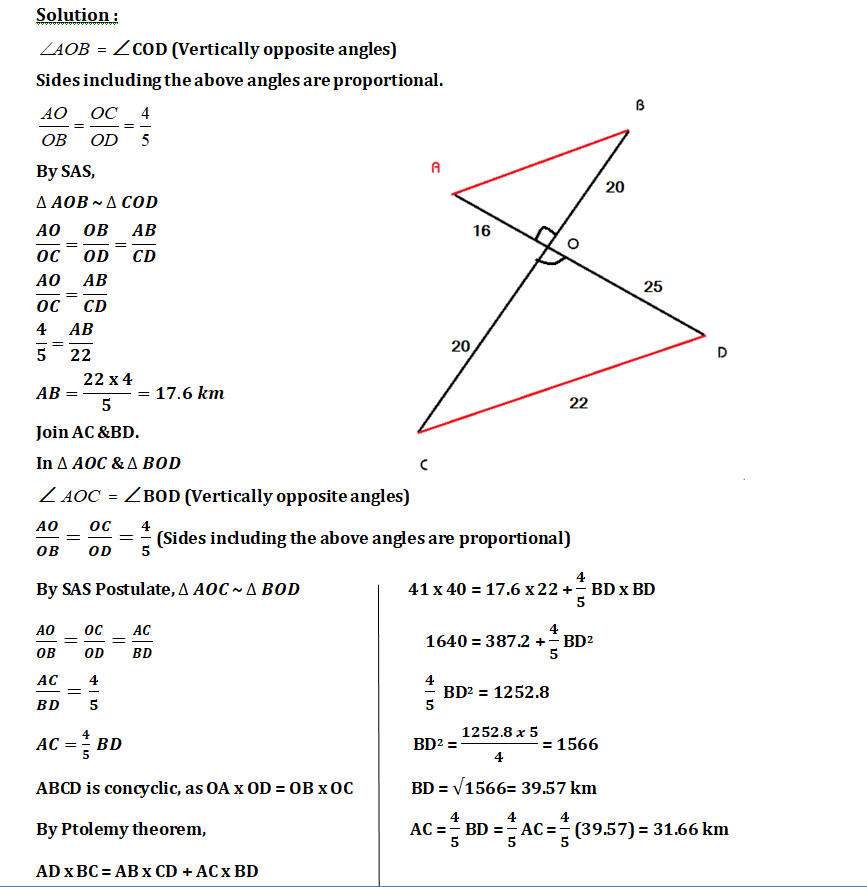
2. Question:
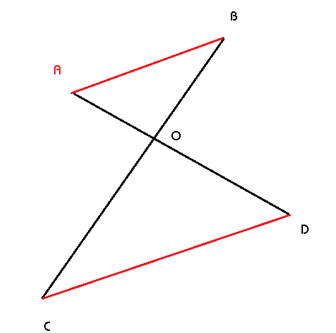
There are four towns, viz A, B, C and D located and connected by roads as shown in the picture. All the roads are on straight lines. Road AD and Road BC meet at O. O is also the midpoint of BC. Road AD = 41 KM, Road BC = 40 KM, Road OD = 25 KM and road DC = 22 KM. Find the length of Road AB.
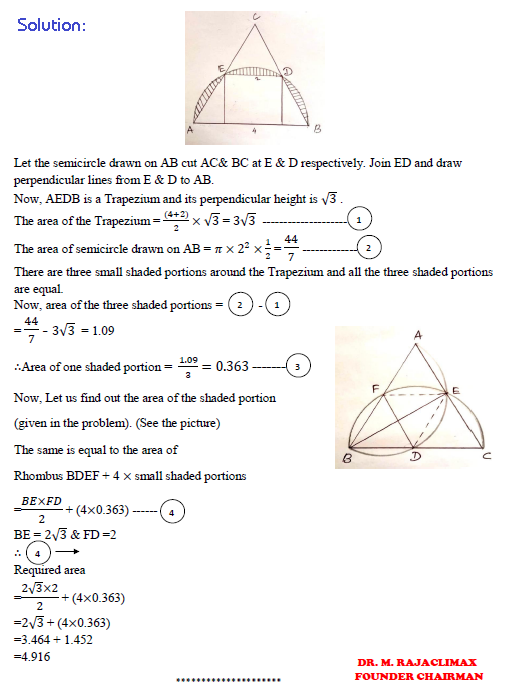
3. Question:
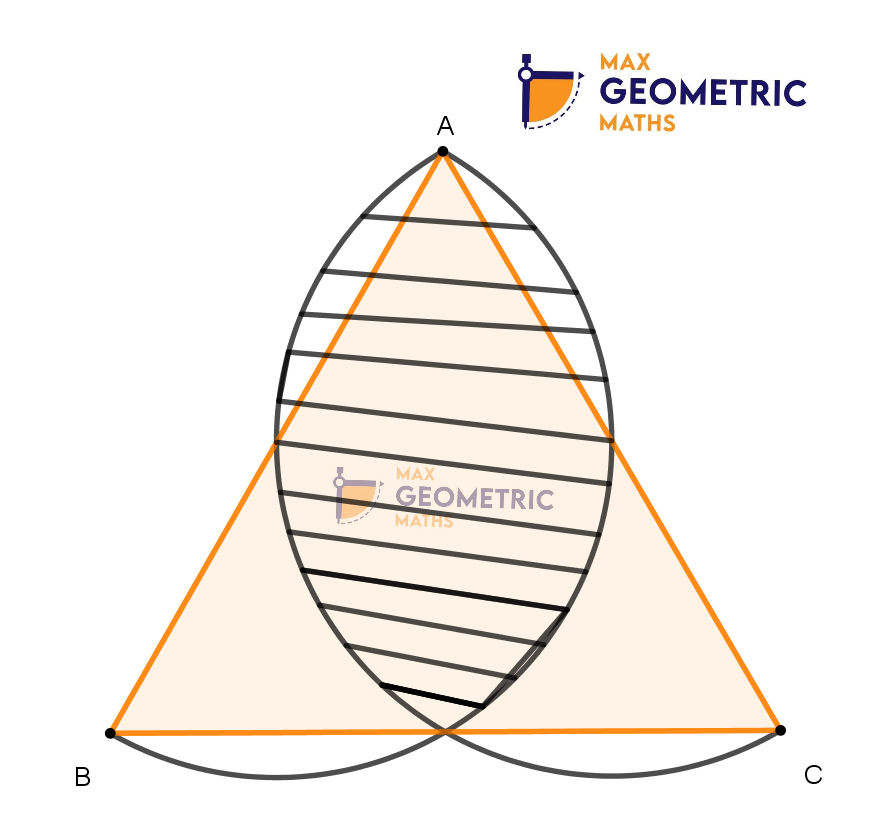
If ABC is an equilateral triangle, find the area of the shaded region.
Author’s Solution for Challenging Problems in Mensuration
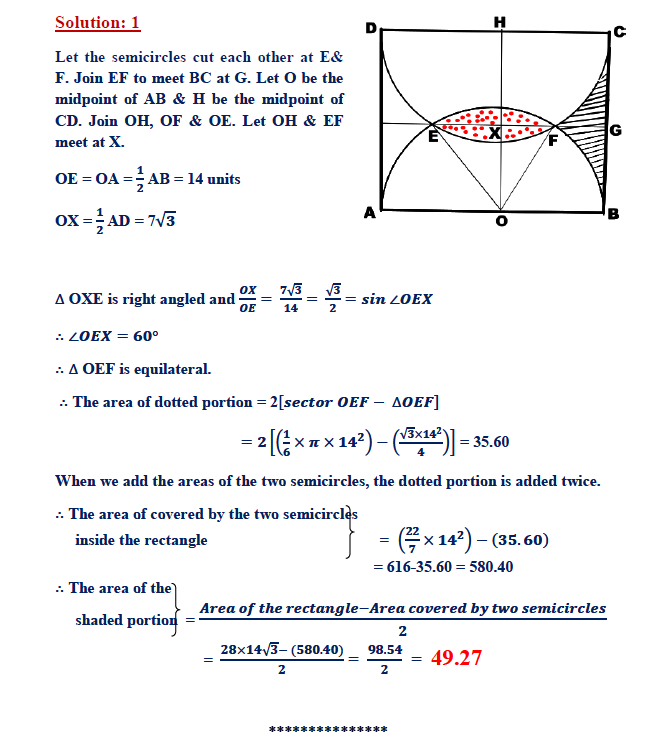
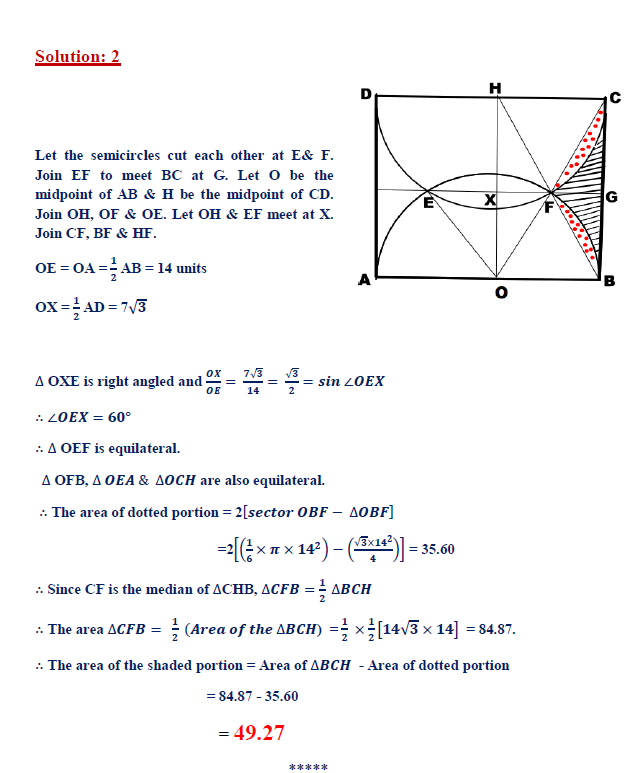
1. Question:
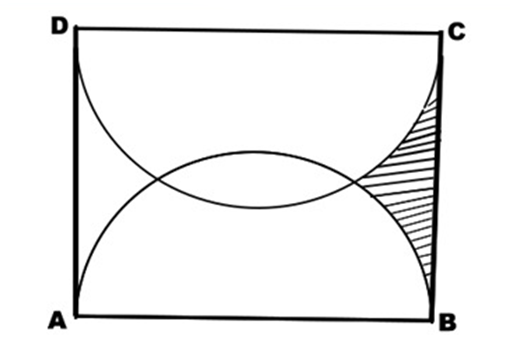
In the figure, ABCD is a rectangle. AB = 28 units & BC = 14√3 units. Semicircles have been using AB & CD as diameters, as shown in the picture. Find the area of the shaded portion.